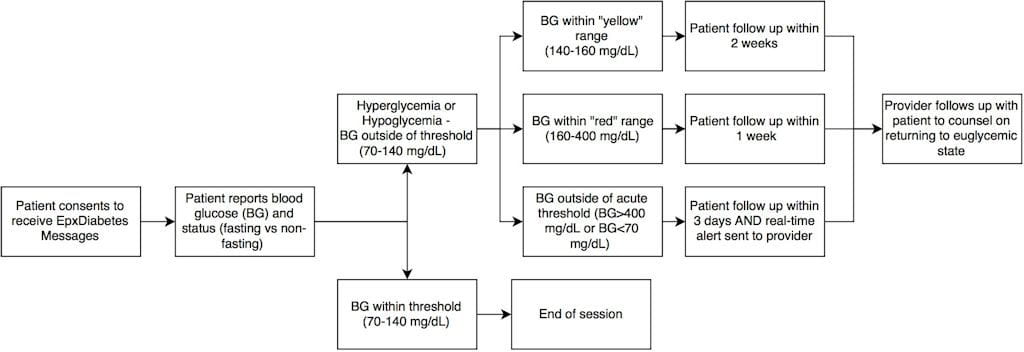
New research shows that using text-messaging intervention with patients that have Type II Diabetes may help reduce HbA1c in patients with high HbA1c baselines (>8%). The study’s objective was to explore the effectiveness of EpxDiabetes, a novel digital health intervention, in improving hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and fasting blood glucose (FBG) among patients with uncontrolled diabetes. EpxDiabetes is a proactive system to help patients track their blood glucose (BG) at intervals set by their physician.
The research publication, Improving Glycemic Control With a Standardized Text-Message and Phone-Based Intervention: A Community Implementation was recently published in JMIR Diabetes. Corresponding author of the paper, Carlos Bernal-Mizrachi, MD, is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Cell Biology and Physiology at Washington University and Chief of Endocrinology at St. Louis VA Medical System.
EpxDiabetes had an average 95.6% patient response rate to messages at least once per month and an average 71.1% response rate to messages at least once per week. Subsequent HbA1c drop with EpxDiabetes use over 4 months was -1.15% (95% CI -1.58 to -0.71) for patients with HbA1c >8% at baseline compared to the change in HbA1c over 4 months prior to the implementation of EpxDiabetes of only -0.005 points (95% CI -0.28 to 0.27), P=.0018.
The results of this study suggest that EpxDiabetes is an inexpensive, low-risk, noninvasive intervention that can be implemented in a variety of settings to accelerate glycemic control for patients with T2DM with baseline HbA1c >8%. The intervention demonstrates high patient engagement sustainable for at least 6 months.